The so-called density refers to the mass of a specific substance under specific conditions per unit volume. The SF6 gas in the SF6 circuit breaker is sealed in a fixed container. Under the rated pressure at 20℃, it has a certain density value. Within the range of all permitted conditions of the circuit breaker's operation, although the pressure of the SF6 gas changes with temperature, the density value of the SF6 gas remains constant. This is because the insulation and arc extinguishing performance of the SF6 circuit breaker largely depends on the purity and density of the SF6 gas. Therefore, the detection of SF6 gas purity and the monitoring of density are particularly important.
The symbol for density is indicated by ρ, and its unit symbol is kg/m3 or g/L. According to the definition of density, the indicated value of the SF6 gas density table should be the unit of density. However, the indicated values for density tables currently produced and used domestically and internationally are borrowed from the unit of pressure: MPa.
According to the ideal gas state equation pv=nRT, it can be seen that pressure p is a linear relation to temperature, shown in the diagram below. When the temperature of the gas in SF6 equipment changes, the values indicated by the pressure gauge also change and cannot accurately reflect the state of the equipment.
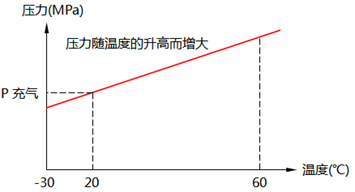
If an ordinary pressure gauge is used to monitor SF6 gas leaks, it would be indistinguishable whether it was due to a real leak or a change in environmental temperature causing a change in SF6 gas pressure. To achieve the purpose of frequently monitoring density, national standards stipulate that SF6 circuit breakers should be equipped with pressure gauges or SF6 gas density gauges and density relays. Pressure gauges or SF6 gas density gauges serve a monitoring function, and density relays serve a control and protection function. The SF6 Relay calibrator is a device specifically used for testing all types of SF6 Relays. Its main function is to measure the action pressure values of SF6 Relay contacts and automatically convert the SF6 gas pressure values and temperature values locked by the SF6 Relay calibrator at the moment of contact action into standard pressure values corresponding to 20℃.
SF6 Relay Structure Principle
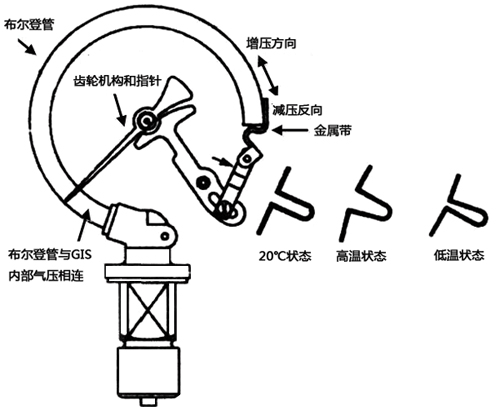
The SF6 relay(table) is mainly composed of spring metal curved tubes, gear mechanisms and pointers, double metal bands, etc. Based on the principle of the spring tube pressure gauge structure, a double metal band that expands and contracts according to environmental temperature changes is added as a temperature compensation device. This causes the spring tube and double metal band to expand and contract in equal and opposite increments along with temperature changes, so the density (pressure) reading does not change with changes in environmental temperature.
The temperature compensation principle of the SF6 Relay structure is as follows:
SF6 Relay
The SF6 relay is actually a pressure relay with temperature compensation, which uses the corresponding pressure value at 20℃ to represent its density value. When the temperature changes, the elastic Bourdon tube and the metal band change simultaneously, thus the pointer display remains unchanged.
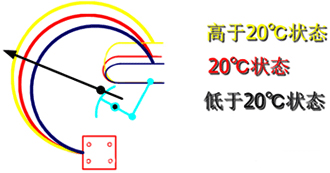
Under constant volume, any pressure change caused solely by temperature change can be compensated for by corresponding changes in the Bourdon tube and the metal strip, so it will not cause the pointer to deflect, thereby ensuring the accuracy of the pressure indicator.
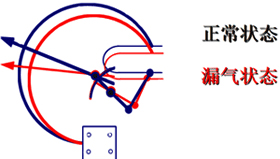
The response of the pressure component to any pressure change caused by non-temperature changes will be transformed into the action of the gas density relay pointer and reflected on the dial, and it can detect pressure values that exceed the minimum or maximum pressure allowed by the system. The image below shows a leakage situation.
Relevant regulations in SF6 electrical equipment maintenance
General requirements for sulfur hexafluoride electrical equipment
According to DL/T728-2013 "Technical Guidelines for Ordering Gas-Insulated Metal-Enclosed Switchgear" and the "High-Voltage Circuit Breaker Operation Regulations" issued by the original Ministry of Energy and other standards, the general requirements for sulfur hexafluoride electrical equipment (mainly referring to SF6 circuit breakers and GIS) are:
Density relays or gas density gauges should be installed to monitor changes in SF6 gas pressure.
Density monitoring devices can be either density gauges or density relays. If a density relay is chosen, a gas density gauge should also be installed.
Check and record the pressure and temperature of the SF6 gas daily.
The new version of the eighteen anti-measures of the State Grid regarding the requirements for the structure of the SF6 relay: The density relay should be installed in a location where it is at the same operating environment temperature as the monitored gas chamber.
If the operating environment temperature is different, it can cause a temperature inconsistency in the compensation of the Bourdon tube and the metal bar, leading to numerical inaccuracies.